Batch LLM Inference
This guide explains how to run batch LLM inference using vLLM on AI-LAB, covering:
- Setting up and running the vLLM container
- Submitting inference jobs via Slurm
What is Batch LLM Inference?
Batch LLM inference refers to processing multiple input prompts in a single inference pass rather than handling them individually. This approach enhances GPU utilization, increases throughput, and reduces overall latency, making it ideal for large-scale text processing tasks on a GPU cluster.
What is vLLM?
vLLM is an optimized inference engine for large language models, designed to improve performance and efficiency. Using vLLM on AI-LAB ensures efficient model execution, particularly when multiple users or jobs run concurrently.
Obtaining a Hugging Face Access Token
Many models on Hugging Face are restricted. To use them, you need an access token.
- Go to Hugging Face and log in or create an account.
-
Navigate to Hugging Face tokens and click Create new token.
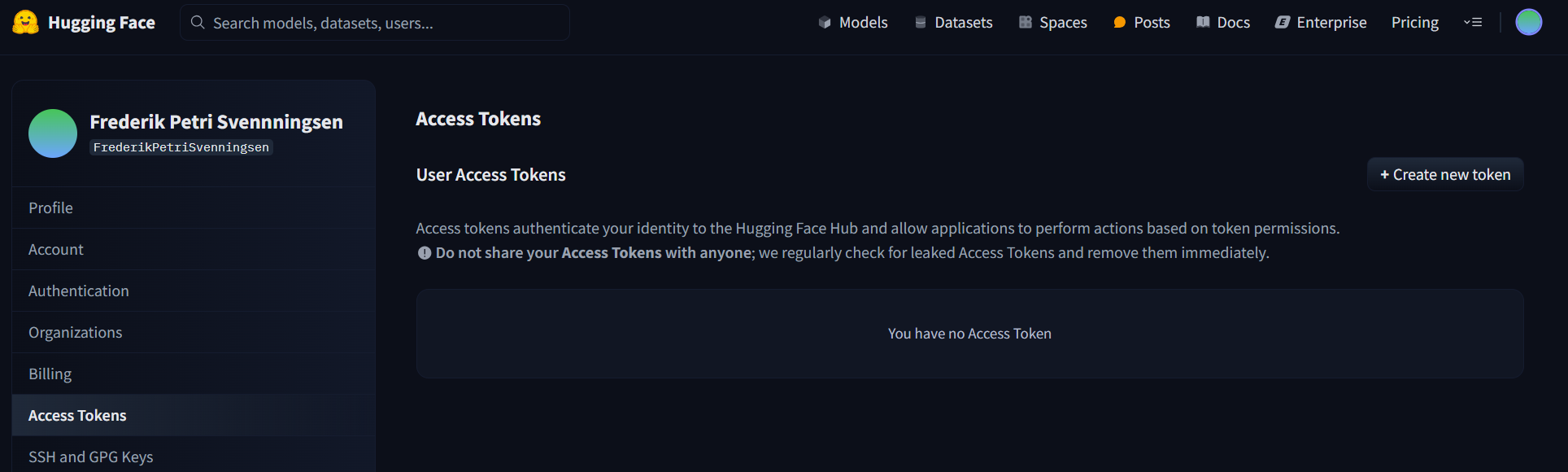
-
Under Token Type, select
Read, enter a Token Name, and click Create Token.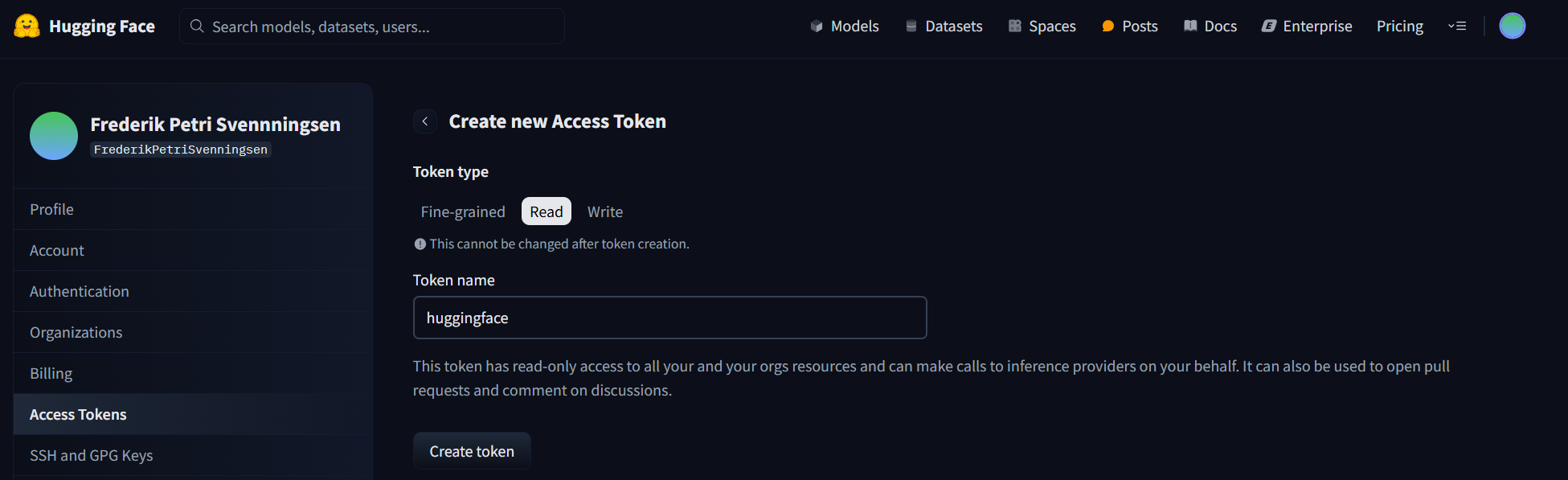
-
Copy the token value and click Done.
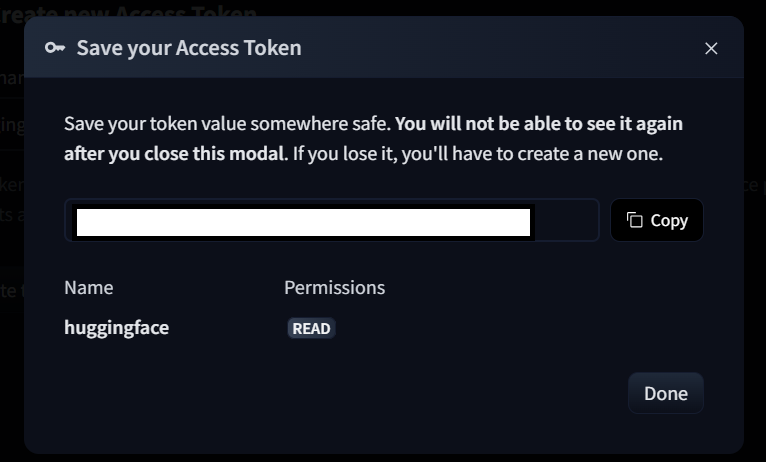
-
On AI-LAB, add the token to your
~/.bashrcto ensure it is always available:echo 'export HF_TOKEN="YOUR_TOKEN"' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc -
Replace
YOUR_TOKENwith your actual token. -
Verify the token is set correctly:
echo $HF_TOKEN
Running vLLM with Slurm
Now that access is set up, we can submit a job via Slurm. The example below demonstrates the basic usage of vLLM to generate text.
Creating a Python Script for vLLM Inference
Create a new file called basic.py with the following code:
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
# Sample prompts.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The president of the United States is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
# Create a sampling params object.
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.8, top_p=0.95)
# Create an LLM instance.
llm = LLM(model="facebook/opt-125m")
# Generate text.
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
# Print results.
for output in outputs:
print(f"Prompt: {output.prompt!r}, Generated text: {output.outputs[0].text!r}")
This script initializes vLLM's engine using the facebook/opt-125m model and generates text based on the given prompts. For more details, refer to the vLLM documentation.
Submitting a Slurm Job
A pre-built vLLM container is available on AI-LAB at /ceph/container/vllm-openai_latest.sif. This container includes vLLM and all necessary dependencies.
Create a Slurm batch script run_vllm.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vllm_textgen
#SBATCH --output=vllm_textgen_output.log
#SBATCH --error=vllm_textgen_error.log
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:1
#SBATCH --mem=40G
#SBATCH --time=04:00:00
singularity exec --nv /ceph/container/vllm-openai_latest.sif python3 basic.py
Submit the job using:
sbatch run_vllm.sh
The job should complete quickly (~2 minutes). Check the vllm_textgen_output.log file for results:
Prompt: 'Hello, my name is', Generated text: ' Joel, my dad is my friend and we are in a relationship. I am'
Prompt: 'The president of the United States is', Generated text: ' speaking out against the release of some State Department documents which show the Russians were involved'
Prompt: 'The capital of France is', Generated text: ' the most populous city in the world, with an annual population of nearly 3 million'
Prompt: 'The future of AI is', Generated text: ' at stake\nThe world is going to change in the next 20 years, and'
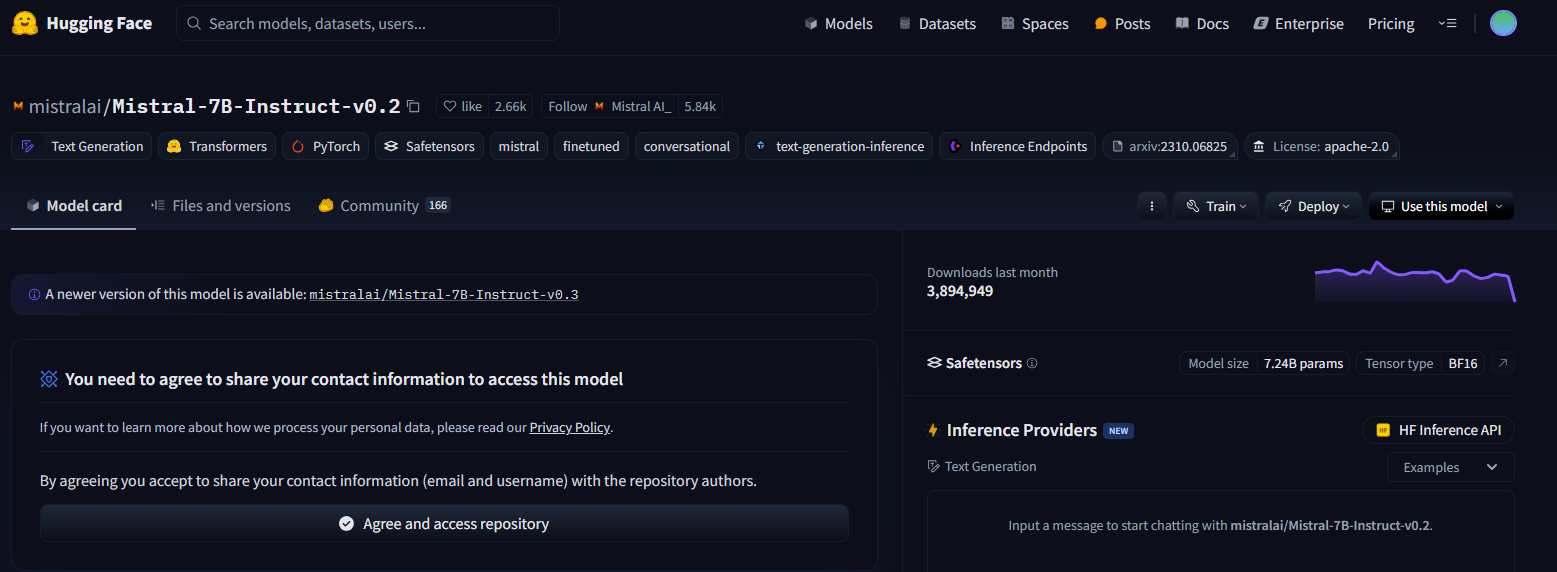
Restricted Model Access Error
If you encounter an error such as:
Access to model meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct is restricted and you are not in the authorized list.
You need to request access on Hugging Face. Visit the model page, such as meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct, and click Agree and access repository.
Additional vLLM Examples
Below are additional examples demonstrating different vLLM use cases. More advanced examples can be found in the vLLM GitHub repository.
chat.py
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from vllm import LLM, EngineArgs
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
def main(args: dict):
# Pop arguments not used by LLM
max_tokens = args.pop("max_tokens")
temperature = args.pop("temperature")
top_p = args.pop("top_p")
top_k = args.pop("top_k")
chat_template_path = args.pop("chat_template_path")
# Create an LLM
llm = LLM(**args)
# Create sampling params object
sampling_params = llm.get_default_sampling_params()
if max_tokens is not None:
sampling_params.max_tokens = max_tokens
if temperature is not None:
sampling_params.temperature = temperature
if top_p is not None:
sampling_params.top_p = top_p
if top_k is not None:
sampling_params.top_k = top_k
def print_outputs(outputs):
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}")
print(f"Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
print("-" * 80)
print("=" * 80)
# In this script, we demonstrate how to pass input to the chat method:
conversation = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hello! How can I assist you today?"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content":
"Write an essay about the importance of higher education.",
},
]
outputs = llm.chat(conversation, sampling_params, use_tqdm=False)
print_outputs(outputs)
# You can run batch inference with llm.chat API
conversations = [conversation for _ in range(10)]
# We turn on tqdm progress bar to verify it's indeed running batch inference
outputs = llm.chat(conversations, sampling_params, use_tqdm=True)
print_outputs(outputs)
# A chat template can be optionally supplied.
# If not, the model will use its default chat template.
if chat_template_path is not None:
with open(chat_template_path) as f:
chat_template = f.read()
outputs = llm.chat(
conversations,
sampling_params,
use_tqdm=False,
chat_template=chat_template,
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = FlexibleArgumentParser()
# Add engine args
engine_group = parser.add_argument_group("Engine arguments")
EngineArgs.add_cli_args(engine_group)
engine_group.set_defaults(model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct")
# Add sampling params
sampling_group = parser.add_argument_group("Sampling parameters")
sampling_group.add_argument("--max-tokens", type=int)
sampling_group.add_argument("--temperature", type=float)
sampling_group.add_argument("--top-p", type=float)
sampling_group.add_argument("--top-k", type=int)
# Add example params
parser.add_argument("--chat-template-path", type=str)
args: dict = vars(parser.parse_args())
main(args)
classify.py
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from argparse import Namespace
from vllm import LLM, EngineArgs
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
def main(args: Namespace):
# Sample prompts.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The president of the United States is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
# Create an LLM.
# You should pass task="classify" for classification models
model = LLM(**vars(args))
# Generate logits. The output is a list of ClassificationRequestOutputs.
outputs = model.classify(prompts)
# Print the outputs.
for prompt, output in zip(prompts, outputs):
probs = output.outputs.probs
probs_trimmed = ((str(probs[:16])[:-1] +
", ...]") if len(probs) > 16 else probs)
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r} | "
f"Class Probabilities: {probs_trimmed} (size={len(probs)})")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = FlexibleArgumentParser()
parser = EngineArgs.add_cli_args(parser)
# Set example specific arguments
parser.set_defaults(model="jason9693/Qwen2.5-1.5B-apeach",
task="classify",
enforce_eager=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
embed.py
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from argparse import Namespace
from vllm import LLM, EngineArgs
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
def main(args: Namespace):
# Sample prompts.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The president of the United States is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
# Create an LLM.
# You should pass task="embed" for embedding models
model = LLM(**vars(args))
# Generate embedding. The output is a list of EmbeddingRequestOutputs.
outputs = model.embed(prompts)
# Print the outputs.
for prompt, output in zip(prompts, outputs):
embeds = output.outputs.embedding
embeds_trimmed = ((str(embeds[:16])[:-1] +
", ...]") if len(embeds) > 16 else embeds)
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r} | "
f"Embeddings: {embeds_trimmed} (size={len(embeds)})")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = FlexibleArgumentParser()
parser = EngineArgs.add_cli_args(parser)
# Set example specific arguments
parser.set_defaults(model="intfloat/e5-mistral-7b-instruct",
task="embed",
enforce_eager=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
generate.py
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from vllm import LLM, EngineArgs
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
def main(args: dict):
# Pop arguments not used by LLM
max_tokens = args.pop("max_tokens")
temperature = args.pop("temperature")
top_p = args.pop("top_p")
top_k = args.pop("top_k")
# Create an LLM
llm = LLM(**args)
# Create a sampling params object
sampling_params = llm.get_default_sampling_params()
if max_tokens is not None:
sampling_params.max_tokens = max_tokens
if temperature is not None:
sampling_params.temperature = temperature
if top_p is not None:
sampling_params.top_p = top_p
if top_k is not None:
sampling_params.top_k = top_k
# Generate texts from the prompts. The output is a list of RequestOutput
# objects that contain the prompt, generated text, and other information.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The president of the United States is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
# Print the outputs.
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}, Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = FlexibleArgumentParser()
# Add engine args
engine_group = parser.add_argument_group("Engine arguments")
EngineArgs.add_cli_args(engine_group)
engine_group.set_defaults(model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct")
# Add sampling params
sampling_group = parser.add_argument_group("Sampling parameters")
sampling_group.add_argument("--max-tokens", type=int)
sampling_group.add_argument("--temperature", type=float)
sampling_group.add_argument("--top-p", type=float)
sampling_group.add_argument("--top-k", type=int)
args: dict = vars(parser.parse_args())
main(args)
score.py
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# Modified by CLAAUDIA, ITS, AAU on 2025-03-04
# - Explicitly set the token before initializing LLM:
from argparse import Namespace
from vllm import LLM, EngineArgs
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
import os
os.environ["HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN"] = os.getenv("HF_TOKEN")
def main(args: Namespace):
# Sample prompts.
text_1 = "What is the capital of France?"
texts_2 = [
"The capital of Brazil is Brasilia.",
"The capital of France is Paris.",
]
# Create an LLM.
# You should pass task="score" for cross-encoder models
model = LLM(**vars(args))
# Generate scores. The output is a list of ScoringRequestOutputs.
outputs = model.score(text_1, texts_2)
# Print the outputs.
for text_2, output in zip(texts_2, outputs):
score = output.outputs.score
print(f"Pair: {[text_1, text_2]!r} | Score: {score}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = FlexibleArgumentParser()
parser = EngineArgs.add_cli_args(parser)
# Set example specific arguments
parser.set_defaults(model="BAAI/bge-reranker-v2-m3",
task="score",
enforce_eager=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
Batch Reasoning with DeepSeek R1
vLLM offers support for reasoning models like DeepSeek R1, which are designed to generate outputs containing both reasoning steps and final conclusions. This guide explains how to use the DeepSeek model with batch processing on. It includes setting up the vLLM server, running inference, and using guided decoding for structured outputs.
Step 1: Writing the Inference Script
Create a Python script (run_inference.py) to interact with the vLLM server:
from openai import OpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Modify OpenAI's API key and API base to use vLLM's API server.
openai_api_key = "EMPTY"
openai_api_base = "http://localhost:8000/v1"
# Initialize OpenAI client for vLLM
client = OpenAI(
api_key=openai_api_key,
base_url=openai_api_base,
)
# List available models
models = client.models.list()
model = models.data[0].id # Assumes the first model is the correct one
# Simple chat completion request
prompt = "What is the capital of France?"
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
extra_body={"guided_regex": "(Paris|London)"}, # Example of guided decoding
)
print("Reasoning:", response.choices[0].message.reasoning_content)
print("Response:", response.choices[0].message.content)
# Guided decoding using JSON schema
class People(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
json_schema = People.model_json_schema()
prompt = "Generate a JSON with the name and age of one random person."
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
extra_body={"guided_json": json_schema},
)
print("Reasoning:", response.choices[0].message.reasoning_content)
print("Response:", response.choices[0].message.content)
Step 2: Creating the Slurm Job Script
Create a Slurm batch script (submit_vllm.sh) to run the inference job:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=vllm_reasoning
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=8
#SBATCH --mem=32G
#SBATCH --time=01:00:00
#SBATCH --output=vllm_output_%j.log
#SBATCH --error=vllm_error_%j.log
# Path to vLLM container
VLLM_CONTAINER="/ceph/container/vllm-openai_latest.sif"
# Start the vLLM server in the background
singularity exec --nv $VLLM_CONTAINER vllm serve deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B \
--enable-reasoning --reasoning-parser deepseek_r1 &
# Get the PID of the server
VLLM_PID=$!
# Wait for server to be ready
echo "Waiting for vLLM server to start..."
while ! curl -s http://localhost:8000/v1/models >/dev/null; do
sleep 2 # Check every 2 seconds
done
# Run inference script
singularity exec --nv $VLLM_CONTAINER python3 run_inference.py
# Stop the server after inference is done
echo "Stopping vLLM server..."
kill $VLLM_PID
Step 3: Submitting the Job
Run the following command to submit the job to Slurm:
sbatch submit_vllm.sh
Step 4: Monitoring and Debugging
Check job status:
squeue --me
Check job logs:
tail -f vllm_output_<job_id>.log
If there are errors, inspect the error log:
tail -f vllm_error_<job_id>.log
This guide provides the foundation for running batch LLM inference using vLLM on AI-LAB. Explore the official vLLM documentation for further customization and optimizations.
